Demand Planning and Forecasting: Mastering Your Supply Chain [2024]
Unlock the power of demand planning and forecasting. Discover key techniques, models, and tools to optimize inventory, reduce costs, and stay ahead in a volatile market.
Unlock the power of demand planning and forecasting. Discover key techniques, models, and tools to optimize inventory, reduce costs, and stay ahead in a volatile market.

If you are truly passionate to run a thriving business, demand planning and forecasting simply cannot be overlooked. Time and time again, we have seen evidence of volatile markets and evolving demands that continue to shake the business world. Having a robust system to predict and plan for such demands can mean a huge difference between thriving and surviving.
In this article, we will discuss the basics of demand and forecasting, explore processes and tools, and show how OneCart can help you with your day to day business.
Demand planning is a strategic process of predicting and managing future customer demand for products or services. When demand planning, your main goal is to balance supply with demand in order to minimize waste and maximize customer satisfaction through order fulfillment. When inventory levels and stock purchases are aligned correctly, businesses will see a significant improvement in operational efficiency.
A demand planner is a professional responsible for creating and managing accurate demand forecasts. The roles of a demand planner include analyzing data, market trends, and customer behavior to identify demand patterns. Demand planners play a big part in procurement, production, and inventory decisions.
Example: If a company sells seasonal products like winter coats, without proper demand planning, they might overstock, leading to extra inventory costs, or understock, resulting in lost sales during the most important sales period.

Demand forecasting is the practice of predicting future customer demand using historical data, market analysis, and statistical methods. Forecasting activities are actually the foundation of demand planning by providing actionable insights into future demand.
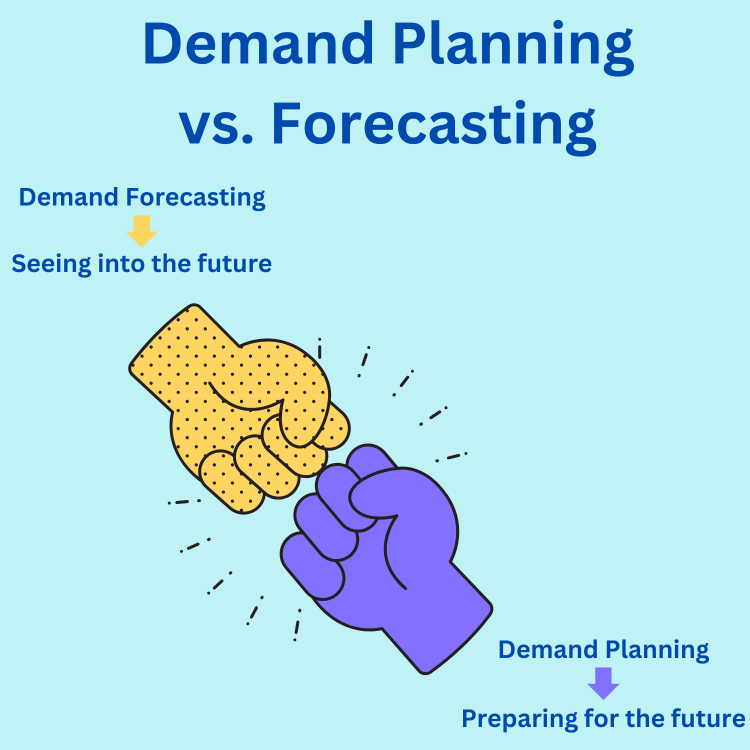
Think of forecasting as seeing into the future and planning as preparing for it.
We can explain things in the simplest way with an example:
When demand planning and forecasting are done correctly together, it allows a business to be proactive rather than to scramble at the last minute to fix any demand issues that come up.
OneCart offers real-time analytics and automated insights to overcome these challenges, ensuring a better operations plan for your business
There are machine learning models available as well, but for our discussion today, we shall focus on statistical models. These mathematics-based models analyze historical data to identify trends and patterns. Two key examples are:
Definition: A forecasting technique that applies decreasing weights to older data points, giving more importance to recent observations. Variants include simple, double, and triple exponential smoothing.
Usage: – Simple exponential smoothing: For data without trend or seasonality. – Double exponential smoothing: For data with trends. – Triple exponential smoothing: For data with both trends and seasonality.
Advantages: – More responsive to recent changes compared to moving averages. – Adjustable smoothing factor for customization based on data characteristics.
Limitations: – Less effective in cases of sudden, unpredictable demand shifts. – Requires parameter tuning for optimal performance.
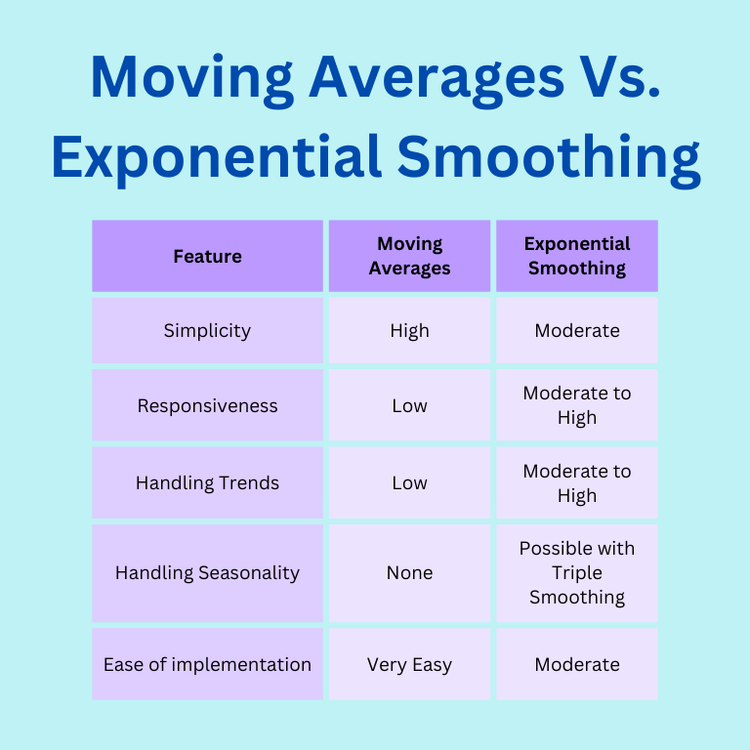
Moving averages and exponential smoothing are both great models to use for planning. However, for a start, moving averages would be the best to start out with as this would allow a business to have a better overall insight over its sales. Any needed adjustments can be made later on, as demand planning is a continuous process.
Gather accurate and relevant data from multiple sources, such as sales records, customer feedback, and market trends, to build a comprehensive dataset. Ensure the data is cleaned to eliminate outliers, duplicates, or errors that could distort the forecasting process.
Use demand forecasting tools, such as statistical models or machine learning, to analyze historical patterns and predict future trends. Consider external factors like seasonality, market conditions, and competitor activity to refine accuracy.
OneCart uses a simple moving average model to better calculate possible stockouts. This feature is a perfect complement for demand planning as it provides more relevant and recent data based on historical sales.
Implement the demand plan by aligning inventory and procurement efforts with the forecasted demand. Continuously monitor performance metrics to identify variances between actual and predicted outcomes.
Identify relationships between demand and external factors, such as prices changes, marketing campaigns, or economic conditions. By understanding these relationships, businesses can make proactive decisions to respond to demand fluctuations effectively.
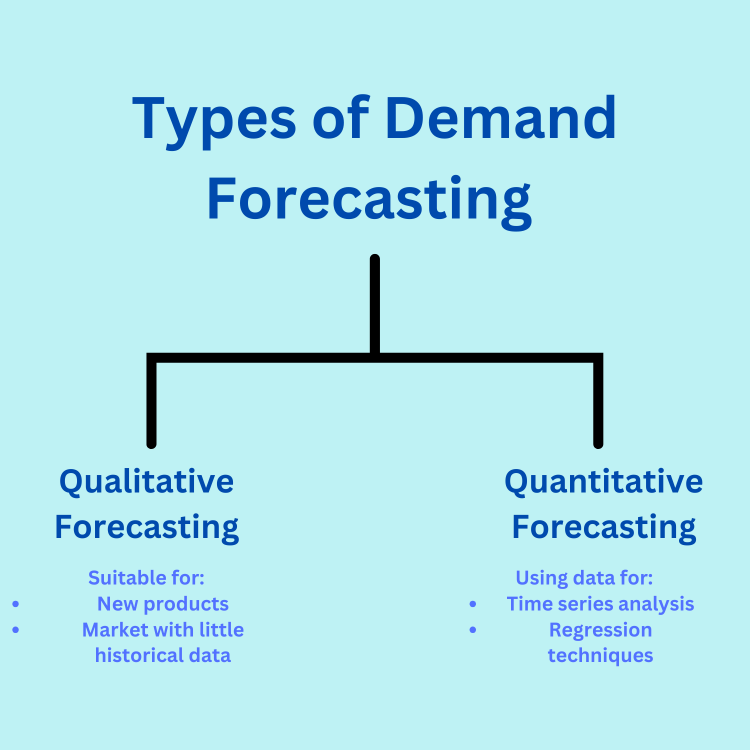
Analyze historical data to identify patterns and make forecasts. This approach is best for stable markets where historical trends are likely to continue. By analyzing the timing and magnitude of demand, businesses can create close-to-perfect forecasts for inventory and resource planning.
Use expert opinions and market insights for situations with limited data. These methods are most appropriate for forecasting new products or entering unfamiliar markets. With the combination of expert insight with available market intelligence, businesses are able to generate informed estimates to guide their decisions. While some may be critical of such methods, it is definitely better than doing nothing at all like jumping into the water without any preparation.
Avoid relying solely on past data. Doing this can lead to inaccurate forecasts when market conditions shift unexpectedly. For instance, unforeseen disruptions like economic shifts, supply chain interruptions, or sudden demand spikes leaves any historical data to be of no use and irrelevant. Thus, go the extra mile and incorporate market trends and real-time insights. The need for the human element cannot be understated in this case.
Stay updated with changing customer preferences and external factors. It is important to monitor market trends and leverage tools like OneCart that provide actionable, real-time data. Failing to account for such external factors can lead to outdated and ineffective demand forecasts.

OneCart is a one stop tool for many of your business activities, which include inventory tracking, order processing and listings management. Such features allow you to have a better overview of your business operations and plan accordingly to avoid any disruptions that could impact your business negatively. The result is high efficiency, better customer satisfaction, and significant cost savings.
Demand planning is the strategic process of predicting and managing future customer demand to align inventory, production, and resources, ensuring efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Demand forecasting is the practice of predicting future customer demand using historical data, market analysis, and statistical methods to provide actionable insights.
Demand forecasting predicts what might happen in the future, while demand planning uses these predictions to take actionable steps.
Forecasting and demand management help optimize inventory levels, reduce costs, and improve customer satisfaction by ensuring product availability.
Demand planning and forecasting are vital for businesses that wish to keep up with changing market conditions. However, it is very important to note that a business should not fully rely on automation to plan future demands. Such tools should be a complement to the human mind. By adopting effective techniques and leveraging automated tools like OneCart, one can focus on other aspects of the business that needs to be handled to maintain and grow operations.
Take the next step in mastering demand planning. Try OneCart today for a free trial and experience automation at its best!
Automate & Scale Your Online Business with OneCart
Start a Free TrialUsed by hundreds of merchants in Singapore & Southeast Asia